Top 5 DevOps automation tools 2018: Docker vs Puppet vs Kubernetes vs Ansible vs Chef
Source – wire19.com
“With our data confirming that 50% of organizations are implementing DevOps, DevOps has reached “Escape Velocity”. On the basis of this data indication, analyst firm Forrester has declared 2018 as “the year of enterprise DevOps”.
The term DevOps is used in multiple ways but in its broadest meaning, DevOps is an operational culture that aims at continuous development & integration and rapid IT service delivery by promoting better communication and improved collaboration between developers and operators. It has become an integral part of different industry sectors- all, from startups to large enterprises are leveraging DevOps tools to support their business processes – project planning until delivery.
With the increasing use of cloud computing and virtualization platforms, the need for new services has increased. The DevOps help organizations respond in a more agile manner to changing business requirements by –
- Automating and monitoring the process of software creation -from integration, testing, releasing to deploying and managing it.
- Reducing the development cycles.
- Increasing the frequency of deployment.
- Streamlining the development and release pipeline.
Thus, using agile DevOps the development and operations team can work together more efficiently and deliver applications and services at faster pace. Also, they can roll out machine level changes in the multi-server environments by using DevOps automation/configuration management tools.
IT industry is flooded with many new DevOps tools which come with vast features and this makes embracing the right DevOps platform or configuration management tool bit difficult.
Walk through this post where we have compared top 5 DevOps tools – Docker vs Kubernetes vs Puppet vs Chef vs Ansible to make things simpler for you.
What is the difference between Docker, Kubernetes, Puppet, Chef and Ansible?
1. Docker

Docker, is a software container technology platform that enables its users to create, deploy, run, and manage applications within the containers. Build on Linux Containers (LxC) it gives freedom to application/infrastructure developers and IT operation teams to create virtual environments and a platform for improved innovation and collaboration.
Docker’s design is modular which allows its users to build applications securely both on-premises and the cloud – it integrates well with the existing environments.
Docker containers run within the kernel of the host machine and they don’t require additional hypervisor load, so they are lightweight. Docker Engine, the client-server application, includes a daemon process (the dockerd command), a REST API to specify the interfaces that programs use to interact to the daemon, and a command line interface (CLI) client.

Docker’s client-server architecture enables the client to work with daemon – which help clients build, pull, run along with distribution of containers.
It’s standardization feature enables developers to analyze and fix bugs in the applications, as well as change Docker images, more efficiently. The users can build a single image and use it across every step during the deployment.
2.Chef
Chef, the configuration management tool delivers fast, scalable, and flexible automation of Web-scale IT. Chef automation tool uses ‘recipes’ for web-server configuration, databases and load balancers. The recipes, which Chef uses to automate infrastructure tasks are in the form of instructions. They help in defining the infrastructure components and how those components can be easily deployed, configured and managed.
Below diagram shows you how Chef code is developed, tested, and deployed.

Chef’s configuration policy enables users to define infrastructure as code, test configuration updates, development infrastructure and cloud instance with its development tools.
Chef, the most notable Infrastructure as Code (IAC) tool, runs the software in client-server mode (Chef-server) and ‘Chef-solo’, the standalone configuration and packages the configurations into JSON files called ‘cookbooks’.
3.Puppet
This flexible, cross-platform and open source DevOps configuration management tool, automates the delivery and operation of a software during its entire lifecycle. Using the puppet
, development and operations teams are able to deliver and operate software (infrastructure, applications) securely and from anywhere.
Puppet increases manageability and productivity. With puppet, users can understand the changes taking place in applications and act on them accordingly with the help of in-depth reports and real-time alerts. Users can identify those changes, and remediate the issues.
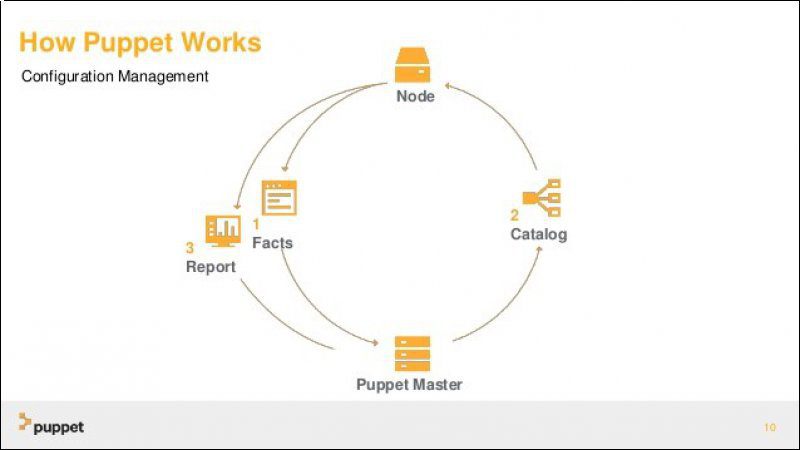
Puppet contains a daemon called Puppet agent that runs on the client servers and it’s another component, the Puppet master contains configuration for all hosts. Both Puppet agent and Puppet master use SSL for secure encryption..
This model-driven software requires limited programming knowledge to use. It treats infrastructure as a code and thus, helps in easier configuration testing & reviewing across all the environments- be it development, test or production.
4. Ansible
Ansible is another simple but powerful DevOps continuous delivery tool. This server and configuration management tool, makes IT automation simple as it ends repetitive tasks and enables faster application deployments, thus allows DevOps teams to perform more strategic work. It automates configuration management, orchestration, application deployment, cloud provisioning, and a number of other IT requirements.

Image source: https://www.ansible.com/integrations/
The ecosystem of Ansible comes with the option to write custom applications. It can be used to make changes in newly-deployed machines and reconfigure them.
Ansible Tower, powered by Red Hat, enables secure management and control of the multi-tier complex deployments and boost productivity.
The difference between Ansible and the above configuration management tools (Puppet, Chef) is that Ansible is mostly used for configuration deployment and is simpler in comparison to other DevOps tools.
5. Kubernetes
Updating and migrating of servers were the two serious issues that enterprises experienced traditionally, as different websites use specific software versions. But today, containerization has solved this problem, successfully. There is a shift underway, the DevOps focus has shifted to writing scalable applications that can be distributed, deployed and run effectively anywhere.

Image source: https://kubernetes.io
As a first step, Docker helped developers to build, ship and run software easily but Kubernetes has helped DevOps to run containers in a cluster, manage applications across different containers while monitoring them effectively. Built on a modular API core, it allows vendors to build systems using core Kubernetes technology.
Designed by Google, Kubernetes is an open source system that provides mechanisms to deploy maintain, and scale containerized applications with automation. Kubernetes is currently maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
Kubernetes allows DevOps to efficiently fulfill customer’s demands by deploying applications predictably and quickly, scaling them, launching new features and limiting hardware usage to only the needed resources.
Being opensource, Kubernetes can be run anywhere and can be used with public, private, hybrid, multi-cloud environments. It is self- healing and offers load balancing and service delivery features along with batch execution and storage orchestration. It also offers features like auto-replication, auto-placement, auto-scaling and auto-restart.
Comparing top 5 DevOps automation tools 2018: Docker vs Chef vs Ansible vs Puppet vs Kubernetes
| Docker | Chef | Ansible | Puppet | Kubernetes |
| Container technology based Linux platform | Automated configuration management tool. | Automated configuration management tool. | Automated configuration management tool. | Automated configuration management tool for containers |
| It is written in Go programming language | It is written in Erlang &Ruby | It uses Python | Ruby-DSL (domain-specific language) language. | Just like Docker, it is also written in Go programming language. |
| Easy to manage, understand and isolate. | Complex from the development perspective. | Easy for configuration management. | Difficult for beginners. | Kubernetes set up requires well-planned efforts when it comes to defining nodes and manual installation. |
| Docker comes with several powerful functionalities and components | It’s similar to Puppet. | Better for front-end developers, where some programming might be needed. | More targeted towards operations – not requiring development background | For developers of modern applications |
| Docker allows configuration for single process at a time, thus making Docker files simpler than bash script for process configuration. | Builds a pipeline of processes. | Produces files in the similar manner as Puppet does. | It may make dependencies complex- may configure more than one process at a time. | Kubernetes brings a lot of complexity as it is a larger project with more moving parts than any other DevOps tool, but that also leads to latency in executing commands, making troubleshooting and monitoring cumbersome. |
Besides the above-mentioned tools, there are few many, namely Nagios, Jenkins, Monit etc.
If you have something to add, please add in the comments section.
