Introduction:
SSH, or secure shell, is an encrypted protocol used to administer and communicate with servers. When working with an Ubuntu server, chances are you will spend most of your time in a terminal session connected to your server through SSH.
In this guide, we’ll focus on setting up SSH keys for an Ubuntu 20.04 installation. SSH keys provide a secure way of logging into your server and are recommended for all users.
Steps:
- Login to the Ubuntu machine using SSH client like Putty
- Run:
sudo -s(This is to be a root user) - Run:
cd /root/
- Verify if .ssh file exists in the /root dir
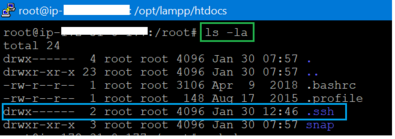
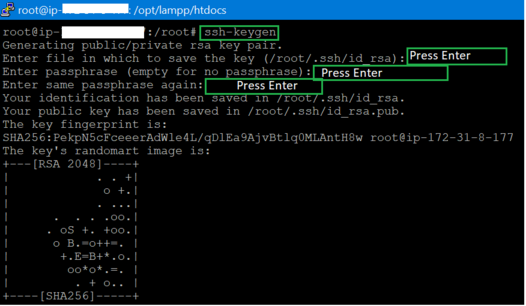
- Generate SSH Key. Command:
ssh-keygen
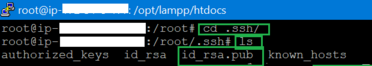
- Move to /root/.ssh directory, Command:
cd .ssh
- Verify if the id_rsa.pub was created successfully using command:
ls
- Reterive the public ssh key to add it in gitlab, github or butbucket using command
more id_rsa.pub
You can simply copy the key and add them in gitlab, github or butbucket

- Git clone to check if you are able to clone the directory after adding the key in gitlab, github or butbucket using commands:
exitsudo git clone git@<Your_Repository_SSH_Clone_URL>