MOTOSHARE 🚗🏍️
Turning Idle Vehicles into Shared Rides & Earnings
From Idle to Income. From Parked to Purpose.
Earn by Sharing, Ride by Renting.
Where Owners Earn, Riders Move.
Owners Earn. Riders Move. Motoshare Connects.
With Motoshare, every parked vehicle finds a purpose.
Owners earn. Renters ride.
🚀 Everyone wins.
What is the main purpose of mysql?
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that is used to store, manage and retrieve data efficiently.
Key features of MySQL:
- Support for multiple storage engines
- Strong data security features
- High performance and scalability
- Support for transactions and indexes
Common uses of MySQL:
- Web applications
- Content management systems (CMS)
- Data warehousing

Why should you consider using mysql?
Here are some reasons why mysql is a popular choice:
1. Reliable and Stable
Mysql has a reputation for being a reliable and stable database management system.
2. Performance
It is known for its performance, especially in read-heavy applications.
3. Scalability
Mysql can scale effectively as your data grows.

What are the key features offered by MySQL?
MySQL is a powerful open-source relational database management system with several key features:
Data Security
MySQL provides robust data security features to protect sensitive information, including user authentication, encryption, and access controls.
Scalability
MySQL is highly scalable, allowing users to efficiently manage large volumes of data and scale their databases as needed.
High Performance
MySQL is optimized for high performance, offering fast query processing and efficient data storage and retrieval.
Reliability
MySQL ensures data integrity and reliability through features such as transactions, crash recovery, and automatic backups.
Flexibility
MySQL supports various data types, storage engines, and platforms, providing flexibility for different types of applications and environments.

Who are the primary users of mysql?
MySQL is a widely-used, open-source relational database management system. The primary users of MySQL include:
- Developers: MySQL is popular among developers for its ease of use, scalability, and strong performance.
- Database Administrators: DBAs use MySQL to manage, maintain, and optimize databases for various applications.
- System Administrators: Sysadmins often deploy and configure MySQL servers to support different services and applications.
- Web Developers: Many web developers choose MySQL for their web applications due to its compatibility with popular programming languages and platforms.

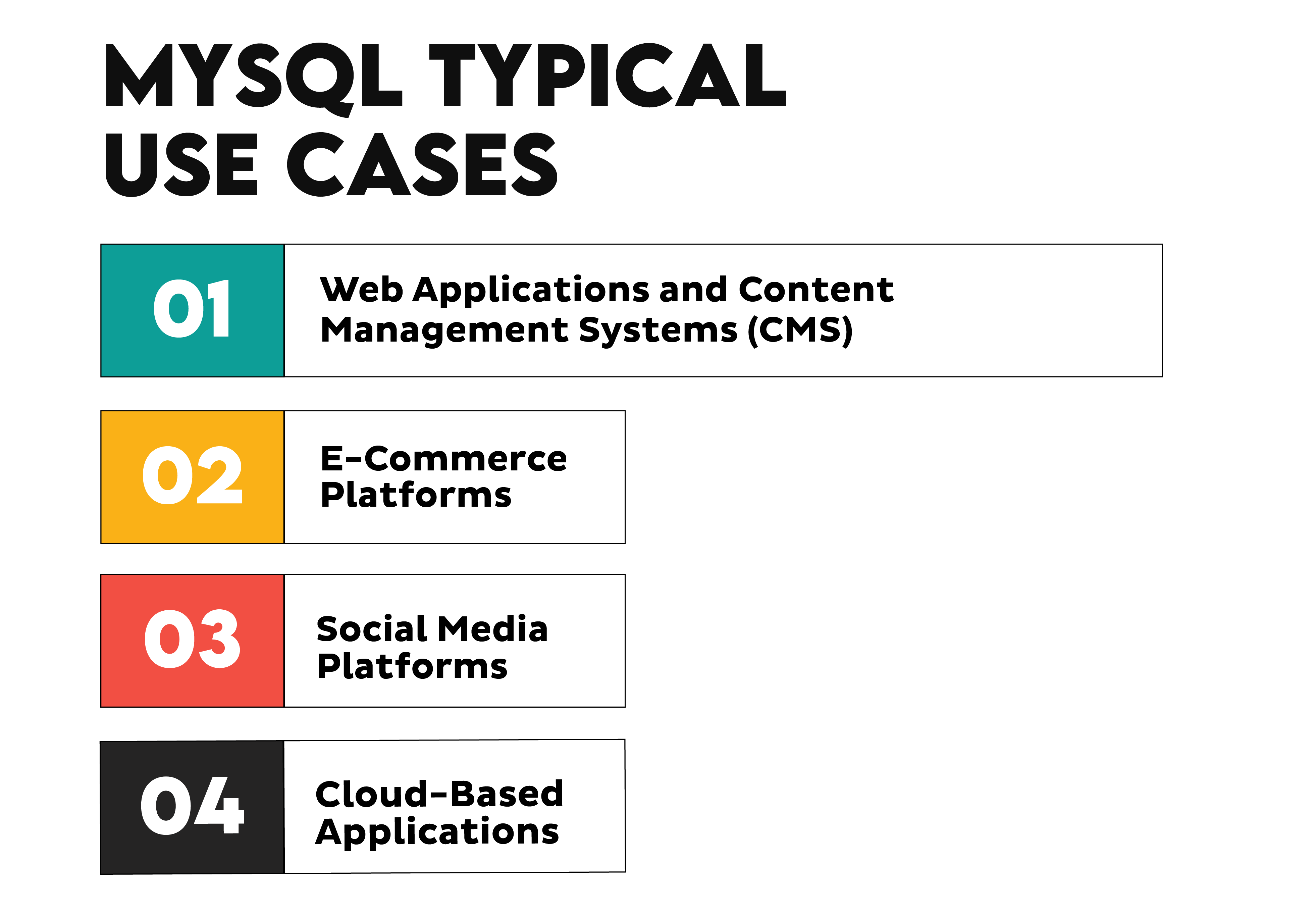
What are the typical use cases for MySQL?
MySQL is a widely used relational database management system that can be utilized in various applications and industries.
Some of the typical use cases for MySQL include:
- Web applications: MySQL is commonly used to power various web applications, from small websites to large-scale platforms.
- Data warehousing: MySQL can be used for storing and managing large volumes of data in data warehouse environments.
- E-commerce platforms: Many e-commerce websites rely on MySQL for their product catalogs, transactions, and customer data.
- Content management systems: MySQL is often integrated into popular content management systems like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla.
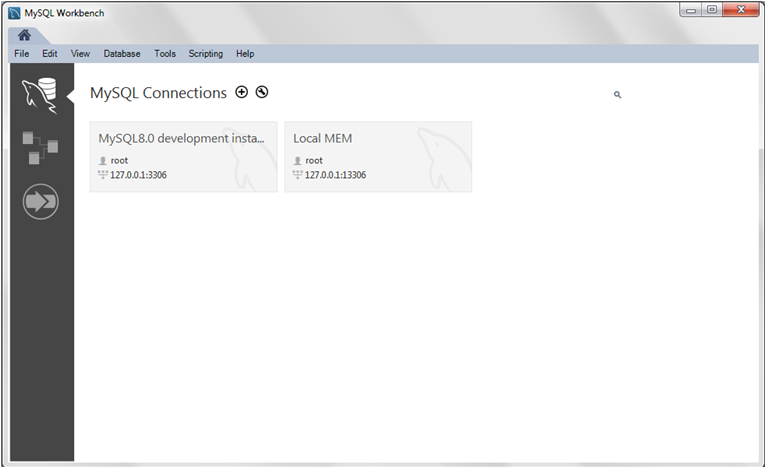
How do you get started with mysql?
To get started with mysql, follow these steps:
- Download and install MySQL: Visit the official MySQL website to download the installer based on your operating system.
- Install MySQL: Follow the installation instructions provided by MySQL to set up the database.
- Start MySQL Server: Once installed, start the MySQL server using the appropriate command.
- Access MySQL: You can access the MySQL database through the command line or a graphical interface like MySQL Workbench.
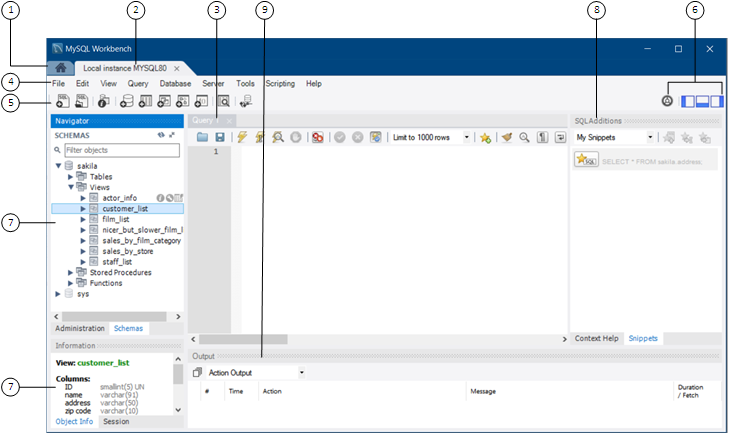
How does it work, in the context of mysql?
MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that stores data in tables with structured relationships between them.
- Schema: MySQL uses a schema to define the structure of the database, including tables, fields, and relationships.
- Queries: Users can interact with MySQL by writing SQL queries to retrieve, update, insert, or delete data.
Connection and Access Control
Users can connect to a MySQL database using various tools such as MySQL Workbench or command-line interfaces.
- Authentication: MySQL enforces access control through user authentication and privileges assigned to each user.
- Network Protocols: MySQL supports different network protocols for communication, such as TCP/IP and Unix sockets.
Where can you deploy or implement mysql?
MySQL can be deployed or implemented in various environments, including:
- On-premises data centers
- Virtual machines
- Cloud platforms such as:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)

What are the limitations or challenges associated with mysql?
MySQL, like any other system, has its own set of limitations and challenges that users may face. Here are some of the common ones:
1. Performance Limitations:
MySQL may face performance limitations when dealing with very large datasets or complex queries.
2. Scalability Challenges:
Scaling MySQL can be challenging, especially when trying to achieve high performance in distributed or cloud-based environments.
3. Lack of Advanced Features:
MySQL may lack some of the advanced features and functionalities compared to other database management systems.
4. Concurrency Control:
MySQL’s concurrency control mechanisms may sometimes lead to bottlenecks and performance issues in highly concurrent environments.
5. Data Integrity Concerns:
Ensuring data integrity and consistency can be challenging in MySQL, especially under high workload conditions.

Comparisons of Other tools with mysql
When it comes to comparing MySQL with other database management systems, there are several factors to consider:
Performance
MySQL is known for its fast performance, but other tools such as PostgreSQL and Oracle can also offer excellent performance based on the specific use case.
Features
While MySQL provides robust features for most common database needs, tools like Microsoft SQL Server and MongoDB offer unique features that might be better suited for certain applications.
Community Support
MySQL has a large and active community that provides support and resources, similar to tools like PostgreSQL and SQLite.
Overall, the choice between MySQL and other database management tools depends on factors such as specific use case, performance requirements, and desired features.
