MOTOSHARE 🚗🏍️
Turning Idle Vehicles into Shared Rides & Earnings
From Idle to Income. From Parked to Purpose.
Earn by Sharing, Ride by Renting.
Where Owners Earn, Riders Move.
Owners Earn. Riders Move. Motoshare Connects.
With Motoshare, every parked vehicle finds a purpose.
Owners earn. Renters ride.
🚀 Everyone wins.

What is Magento?
Magento is a leading open-source e-commerce platform designed to enable merchants to build highly customizable, scalable, and feature-rich online stores. Originally released in 2008 and later acquired by Adobe, Magento has evolved into one of the most flexible and robust e-commerce solutions, serving small businesses to enterprise-level organizations globally.
Magento’s key strength lies in its modular architecture, enabling developers and merchants to extend or modify the core functionality without impacting the base system. The platform supports complex product types, multi-store capabilities, advanced marketing tools, and seamless integration with various payment gateways, shipping providers, and third-party services.
There are two primary editions of Magento:
- Magento Open Source: A free version suitable for startups and small to medium businesses, allowing full access to the platform’s core features.
- Magento Commerce (Adobe Commerce): A paid, enterprise-grade solution that includes advanced functionalities, cloud hosting, security features, and dedicated support.
Magento supports both B2C and B2B commerce and has extensive community support, a rich ecosystem of extensions, and professional services.
Major Use Cases of Magento
Magento is used widely due to its flexibility and power. Some major use cases include:
1. Traditional Online Retail Stores
Magento enables retailers to showcase extensive product catalogs with configurable, bundled, and downloadable products. It supports complex pricing, discounts, and promotional campaigns essential for retail success.
2. B2B E-commerce
Magento provides B2B-specific features like company accounts, custom pricing, quick order forms, and quote requests. These tools streamline business purchasing processes and enhance enterprise client experiences.
3. Multi-Store and Multi-Vendor Platforms
Merchants can operate multiple storefronts from a single Magento installation, each with distinct branding, products, and customer groups. Marketplaces can be built on Magento with multi-vendor extensions.
4. Mobile Commerce (M-Commerce)
Magento supports responsive themes and Progressive Web Apps (PWA), enabling merchants to deliver fast, app-like shopping experiences on mobile devices.
5. International E-commerce
Magento’s native multi-currency, multi-language, and localized tax and shipping support help merchants expand globally while complying with local regulations.
6. Subscription and Digital Goods
Merchants can sell subscriptions, digital downloads, and services alongside physical goods, offering flexibility in product offerings.
7. Custom Personalized Shopping Experiences
Magento’s modular design allows integration of AI-powered recommendations, personalized promotions, and loyalty programs to increase customer engagement.
How Magento Works Along with Architecture
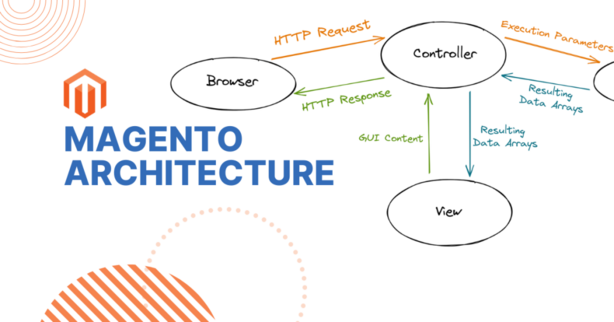
Magento’s architecture is sophisticated and built for extensibility, performance, and scalability. Understanding its architecture is key to effective deployment and customization.
High-Level Architectural Overview
Magento’s architecture follows a modular MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern with layered components:
1. Presentation Layer (Frontend)
- The frontend displays the storefront to customers and manages user interactions.
- Uses technologies such as PHP, HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, Knockout.js, RequireJS, and LESS.
- Supports themes and templates to customize the look and feel.
2. Business Logic Layer (Model + Service Layer)
- Contains the core logic for handling business rules such as product management, pricing, inventory, promotions, checkout, and customer accounts.
- Encapsulated in PHP classes within modules for clean separation and reusability.
3. Data Access Layer (Model and Resource Models)
- Interacts with the underlying database, encapsulating SQL queries and entity management.
- Magento uses a combination of relational database models, including the Entity-Attribute-Value (EAV) model for flexible product attributes.
4. Database Layer
- Magento primarily uses MySQL or MariaDB databases.
- Uses database indexing for optimizing queries and caching for faster performance.
5. API Layer
- Exposes RESTful and GraphQL APIs for integration with third-party systems, mobile apps, and headless commerce setups.
6. Cache and Session Management
- Employs caching technologies like Redis, Varnish, and built-in caches to reduce database load and improve page load speeds.
- Manages user sessions securely.
7. Admin Panel (Backend)
- A fully featured admin interface for store configuration, product management, order processing, customer management, and reporting.
8. Modularity and Extensibility
- Magento’s system is built on modularity, allowing installation of extensions that add or modify functionality without affecting the core codebase.
- Dependency Injection and Service Contracts allow for customization while maintaining upgrade safety.
Basic Workflow of Magento
Magento’s workflow encompasses the customer journey and administrative processes:
1. Product Catalog Management
Store administrators create and configure products, categorize them, set prices, and assign inventory levels.
2. Customer Browsing and Search
Visitors browse the catalog, filter by attributes, or search products using Elasticsearch-powered search for fast results.
3. Shopping Cart and Checkout
Customers add products to their carts and proceed through a multi-step checkout process where shipping, taxes, and payment options are calculated.
4. Order Placement and Processing
Magento handles order validation, payment authorization, and generates order records for fulfillment.
5. Inventory and Shipping
Inventory levels are updated automatically, and shipping integrations allow label printing and tracking.
6. Customer Account Management
Customers can track orders, manage addresses, view purchase history, and manage preferences.
7. Marketing and Promotions
Merchants use Magento’s tools to create coupons, discounts, cross-sells, and up-sells.
8. Reporting and Analytics
Store owners analyze sales trends, customer behavior, and inventory via dashboards and reports.
Step-by-Step Getting Started Guide for Magento
Step 1: Prepare Your Environment
- Ensure you have a compatible server stack (Apache/Nginx, PHP 7.4+, MySQL 5.7+, Composer).
- Meet Magento’s system requirements including Elasticsearch for catalog search.
Step 2: Download and Install Magento
- Install via Composer for the latest stable version:
composer create-project --repository-url=https://repo.magento.com/ magento/project-community-edition magento
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Set file permissions and configure your web server.
Step 3: Create Database
- Create a MySQL/MariaDB database and user for Magento.
Step 4: Run Magento Installation Wizard or CLI Install
Using CLI:
php bin/magento setup:install \
--base-url="http://yourdomain.com/" \
--db-host="localhost" \
--db-name="magento_db" \
--db-user="db_user" \
--db-password="db_pass" \
--admin-firstname="Admin" \
--admin-lastname="User" \
--admin-email="admin@domain.com" \
--admin-user="admin" \
--admin-password="StrongPassword123" \
--language="en_US" \
--currency="USD" \
--timezone="America/New_York" \
--use-rewrites="1"
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 5: Access Admin Panel
- Log in to
http://yourdomain.com/adminwith admin credentials.
Step 6: Configure Store Settings
- Set locale, currencies, taxes, payment gateways, and shipping methods.
Step 7: Add Products and Categories
- Use the admin interface to populate your catalog.
Step 8: Choose and Customize Themes
- Install themes or build custom themes for unique branding.
Step 9: Install Extensions
- Enhance your store with extensions from Magento Marketplace.
Step 10: Test Your Store
- Perform functional tests on checkout, payment, and navigation.
Step 11: Launch Your Store
- Go live and monitor performance using Magento’s built-in tools.