MOTOSHARE 🚗🏍️
Turning Idle Vehicles into Shared Rides & Earnings
From Idle to Income. From Parked to Purpose.
Earn by Sharing, Ride by Renting.
Where Owners Earn, Riders Move.
Owners Earn. Riders Move. Motoshare Connects.
With Motoshare, every parked vehicle finds a purpose.
Owners earn. Renters ride.
🚀 Everyone wins.
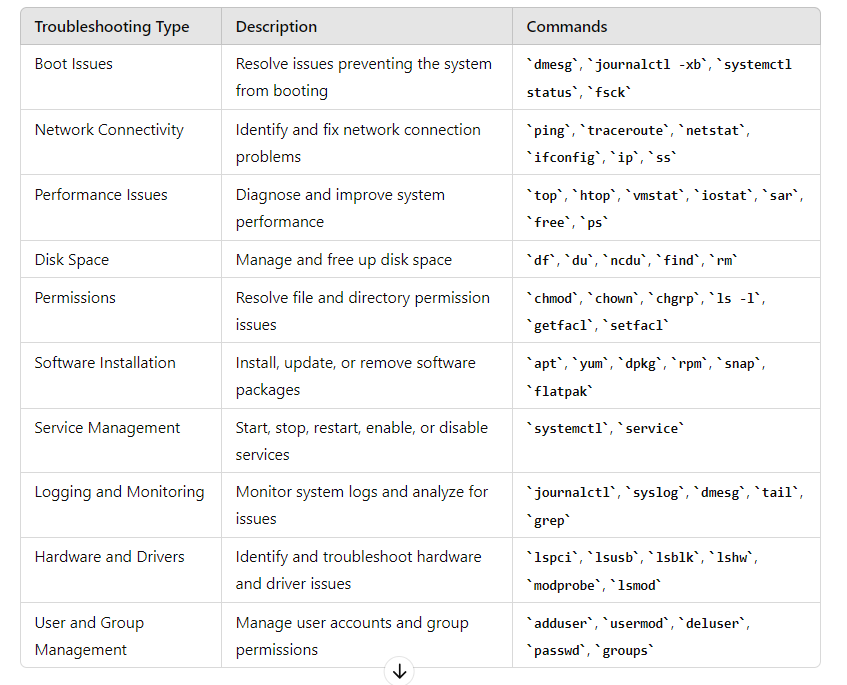
Boot Issues: Check boot logs (dmesg, journalctl -xb), bootloader configuration (grub.cfg).
Networking: Verify network configuration (ifconfig, ip addr), check connectivity (ping, traceroute), review firewall settings (iptables).
Performance: Monitor system resources (top, htop, vmstat), check disk usage (df -h), identify CPU or memory bottlenecks.
Disk Space: Check disk usage (df -h), identify large files/directories (du -sh).
Permissions: Verify file/directory permissions (ls -l, getfacl), ensure correct ownership (chown, chgrp).
Software Installation: Check package installation (dpkg, rpm, apt, yum), verify dependencies.
Service Management: Restart services (systemctl restart <service>), check service status (systemctl status <service>).
Logging and Monitoring: Review system logs (/var/log), use monitoring tools (sar, sysstat, Prometheus, Grafana).
Hardware and Drivers: Check hardware status (lspci, lsusb), verify driver status (lsmod, modprobe).
User and Group Management: Verify user permissions (groups, id), manage user accounts (adduser, usermod, deluser).Code language: HTML, XML (xml)- dmesg – Displays the kernel ring buffer messages.
- journalctl – Views and manages systemd journal logs.
- ls – Lists directory contents.
- ps – Lists currently running processes.
- top – Displays real-time system information, including CPU and memory usage.
- htop – Interactive process viewer and system monitor.
- df – Shows disk space usage.
- du – Displays disk usage for files and directories.
- free – Shows memory and swap usage.
- uptime – Displays system uptime and load averages.
- netstat – Shows network statistics, connections, and routing tables.
- ifconfig – Displays network interface configuration.
- ip – Shows or manipulates routing, devices, policy routing, and tunnels.
- ping – Sends ICMP Echo Request packets to a network host.
- traceroute – Prints the route packets take to a network host.
- lsof – Lists open files and the processes that opened them.
- ps – Lists information about processes.
- kill – Sends a signal to terminate processes.
- systemctl – Controls systemd services (e.g., start, stop, enable, disable).
- grep – Searches for patterns in files or input.
- tail – Outputs the last part of files.
- cat – Concatenates and displays files.
- less – Displays text files with pagination.
- find – Searches for files and directories.
- cp – Copies files and directories.
- mv – Moves or renames files and directories.
- rm – Removes files and directories.
- chmod – Changes file permissions.
- chown – Changes file owner and group.
- ssh – Securely connects to a remote server.
[…] https://www.bestdevops.com/how-to-troubleshoot-in-linux […]