MOTOSHARE 🚗🏍️
Turning Idle Vehicles into Shared Rides & Earnings
From Idle to Income. From Parked to Purpose.
Earn by Sharing, Ride by Renting.
Where Owners Earn, Riders Move.
Owners Earn. Riders Move. Motoshare Connects.
With Motoshare, every parked vehicle finds a purpose.
Owners earn. Renters ride.
🚀 Everyone wins.
To Create your Own Widget in Flutter, Just Follow the Below Steps.
- New Dart file for your widget creation:
To select a folder in your project hierarchy, use the right mouse button.
Choose “New” then “File.”
Enter a file name ending in “.dart,” for example, “my_custom_widget.”
- Open the newly created file and import the necessary packages:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Define your custom widget by creating a new class that extends StatelessWidget or StatefulWidget:
If your widget doesn’t need to maintain any internal state, extend StatelessWidget:
class MyCustomWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// Widget implementation
}
}
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- If your widget needs to maintain internal state and be updated dynamically, extend StatefulWidget:
class MyCustomWidget extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_MyCustomWidgetState createState() => _MyCustomWidgetState();
}
class _MyCustomWidgetState extends State<MyCustomWidget> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// Widget implementation
}
}
Code language: PHP (php)- Implement the build method within your custom widget class:
Inside the build method, return the UI representation of your widget by creating and configuring Flutter widgets:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
// Widget configuration
);
}
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)- Customize your widget by adding child widgets, applying styles, and configuring properties:
The structure and look of your widget can be specified using pre-existing Flutter widgets or by developing a bespoke widget within the build function.
Widgets can be nestled inside of other widgets to make intricate designs and architectures.
- Optionally, add properties to your custom widget for customization:
- Define properties as instance variables within your widget class, and pass values to these properties when using your widget.
- Use these property values within the build method to customize the behavior or appearance of your widget.
- Use your custom widget in other parts of your Flutter app:
- Import the file where your custom widget is defined.
- Add an instance of your custom widget to the widget tree, just like any other Flutter widget:
MyCustomWidget(),
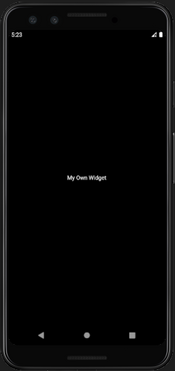
See Output Below