MOTOSHARE 🚗🏍️
Turning Idle Vehicles into Shared Rides & Earnings
From Idle to Income. From Parked to Purpose.
Earn by Sharing, Ride by Renting.
Where Owners Earn, Riders Move.
Owners Earn. Riders Move. Motoshare Connects.
With Motoshare, every parked vehicle finds a purpose.
Owners earn. Renters ride.
🚀 Everyone wins.

What is Tkinter?
Tkinter is the standard graphical user interface (GUI) toolkit bundled with Python. It provides a powerful yet easy-to-use interface for building desktop applications with windows, buttons, menus, text fields, and other common GUI elements. Tkinter acts as a Python wrapper around the mature and widely used Tcl/Tk GUI toolkit, originally developed in the early 1990s. Because Tkinter ships with Python by default, it is the go-to solution for developers wanting to create cross-platform desktop applications without requiring additional installations.
Tkinter enables Python programmers—whether beginners or experts—to develop fully interactive, event-driven applications. Its simple API lowers the barrier to entry for GUI programming, while its extensibility allows for complex applications. Tkinter applications run consistently across Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it an excellent choice for platform-independent software development.
Tkinter supports various widgets including:
- Labels, Buttons, Entry fields, Checkbuttons, Radiobuttons
- Frames, Menus, Canvas (for drawing), Scrollbars
- Dialogs for file selection, message boxes, and color selection
Moreover, Tkinter integrates well with other Python libraries, enabling developers to build applications with graphics, charts, and multimedia.
What Are the Major Use Cases of Tkinter?
Tkinter’s versatility lends itself to many real-world applications and scenarios:
1. Educational Purposes and Prototyping
Due to its simplicity, Tkinter is widely used in educational settings to introduce GUI programming concepts. Beginners learn about event-driven programming, widget hierarchies, and layout management with Tkinter. It is also a popular choice for rapid prototyping of desktop applications, allowing developers to quickly build and test UI ideas.
2. Small to Medium Desktop Applications
Many developers build productivity tools such as calculators, form entry systems, text editors, and simple database front-ends using Tkinter. These applications benefit from Tkinter’s built-in widgets and straightforward event handling.
3. Custom Tools and Utilities
System administrators and developers often create custom utilities, configuration panels, and monitoring dashboards with Tkinter. Its cross-platform nature ensures these tools can run on different operating systems without modification.
4. Cross-Platform Application Development
Tkinter’s reliance on Tcl/Tk means applications behave consistently across platforms, making it suitable for apps targeting multiple operating systems without significant code changes.
5. Integration with Scientific and Data Applications
Tkinter can be combined with libraries like Matplotlib for embedding plots, Pillow (PIL) for image processing, and OpenCV for computer vision tasks, allowing scientists and engineers to build interactive data visualization tools.
How Tkinter Works: Architecture and Components
Tkinter’s architecture is layered, bridging Python code with the Tcl/Tk GUI toolkit and the operating system’s native windowing system.
1. Python Layer (Tkinter Module)
Tkinter provides Python classes that represent GUI widgets and application windows. These classes simplify widget creation, configuration, and event binding in a Pythonic manner.
Example of widget creation:
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
button = tk.Button(root, text="Click Me")
button.pack()
root.mainloop()
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)2. Tcl Interpreter
Tkinter communicates with an embedded Tcl interpreter. Python commands are converted into Tcl commands, which are executed by this interpreter.
3. Tk GUI Toolkit
Tk provides the actual GUI elements, rendering widgets on screen and managing user interactions. It abstracts the differences between platforms, handling drawing and input events.
4. Operating System Windowing System
Tk interacts with the native windowing system (Win32 API on Windows, Quartz on macOS, X11 on Linux) to display windows, capture user input, and manage event queues.
Key Tkinter Components and Widget Types
- Tk() — The main application window
- Frame — A container widget used to group other widgets
- Label — Displays text or images
- Button — Triggers actions when clicked
- Entry — Single-line text input field
- Text — Multi-line text editor
- Checkbutton — Checkbox for binary options
- Radiobutton — Allows selection of one option from a set
- Canvas — Drawing surface for graphics, shapes, and images
- Menu — Dropdown menus for application commands
- Scrollbar — Scrollbars for navigating content
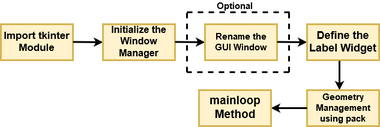
What Are the Basic Workflows of Tkinter?
Building a Tkinter application typically follows these steps:
1. Initialize the Main Window
Create the root window, which acts as the main container for all widgets:
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("My Tkinter App")
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)2. Create and Configure Widgets
Widgets are instantiated and configured with options like text, colors, fonts, and sizes.
label = tk.Label(root, text="Welcome to Tkinter")
label.pack(pady=10)
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)3. Organize Widgets with Geometry Managers
Tkinter uses three geometry managers to control widget placement:
- pack() — Packs widgets in blocks before or after each other
- grid() — Arranges widgets in a table-like structure with rows and columns
- place() — Positions widgets at absolute locations
Example:
button = tk.Button(root, text="Click Me")
button.grid(row=0, column=0)
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)4. Bind Events and Define Callbacks
Widgets respond to user events like mouse clicks or key presses through event binding:
def on_click():
print("Button clicked!")
button = tk.Button(root, text="Click", command=on_click)
button.pack()
Code language: PHP (php)5. Start the Main Event Loop
The event loop listens for user interactions and dispatches events to callbacks:
root.mainloop()
Code language: CSS (css)Step-by-Step Getting Started Guide for Tkinter
Step 1: Verify Python Installation
Ensure Python 3.x is installed on your machine. Tkinter is included by default in most standard Python installations.
Step 2: Write Your First Tkinter Program
Create a Python file (e.g., hello_tkinter.py) with the following content:
import tkinter as tk
def greet():
print("Hello from Tkinter!")
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("First Tkinter App")
root.geometry("300x150")
label = tk.Label(root, text="Welcome to Tkinter!", font=("Helvetica", 16))
label.pack(pady=10)
button = tk.Button(root, text="Greet", command=greet)
button.pack()
root.mainloop()
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Run the script:
python hello_tkinter.py
Code language: CSS (css)You should see a window with a label and a button that prints a message when clicked.
Step 3: Experiment with Widgets
Add more widgets like Entry, Checkbutton, and Radiobutton to enhance your application.
entry = tk.Entry(root)
entry.pack(pady=5)
Step 4: Use Layout Managers
Try using grid() to place widgets in a grid:
label.grid(row=0, column=0)
entry.grid(row=0, column=1)
Step 5: Handle User Input
Retrieve input from widgets to make interactive applications:
def show_input():
user_text = entry.get()
print("You entered:", user_text)
button = tk.Button(root, text="Show Input", command=show_input)
button.pack()
Code language: PHP (php)Step 6: Explore Advanced Features
- Use
Canvasto draw graphics - Create menus and dialog boxes
- Integrate with other Python libraries for complex tasks