MOTOSHARE 🚗🏍️
Turning Idle Vehicles into Shared Rides & Earnings
From Idle to Income. From Parked to Purpose.
Earn by Sharing, Ride by Renting.
Where Owners Earn, Riders Move.
Owners Earn. Riders Move. Motoshare Connects.
With Motoshare, every parked vehicle finds a purpose.
Owners earn. Renters ride.
🚀 Everyone wins.

What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on building systems that can learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. Unlike traditional programming, where explicit instructions dictate the behavior of software, machine learning enables models to improve automatically through experience.
At its essence, machine learning involves feeding data into algorithms that learn a mathematical function mapping inputs to desired outputs. Over time, these models generalize from the examples they have seen, allowing them to make predictions or take actions on new, unseen data. ML is broadly categorized into:
- Supervised Learning: The algorithm is trained on labeled data, meaning each input comes with a known output (e.g., predicting house prices based on features like size and location).
- Unsupervised Learning: The model identifies patterns or groupings in data without explicit labels (e.g., customer segmentation).
- Reinforcement Learning: Models learn by interacting with an environment, receiving rewards or penalties based on their actions, refining their strategy over time (e.g., game-playing AI).
Machine learning’s ability to analyze complex data and extract insights has made it pivotal in modern technology.
Major Use Cases of Machine Learning
Machine learning’s versatility allows it to be applied across a wide range of industries and problem domains. Some prominent use cases include:
1. Healthcare:
- Disease Diagnosis: ML models analyze medical images like X-rays and MRIs to detect anomalies such as tumors.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting patient outcomes and potential complications.
- Drug Discovery: Accelerating the identification of new compounds by predicting molecular behavior.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments based on genetic and clinical data.
2. Finance:
- Fraud Detection: Identifying unusual transactions to prevent fraud.
- Credit Scoring: Assessing creditworthiness using customer data.
- Algorithmic Trading: Using ML to analyze market data and execute trades.
- Risk Management: Predicting and mitigating financial risks.
3. Retail and E-commerce:
- Recommendation Engines: Suggesting products based on user behavior and preferences.
- Inventory Management: Forecasting demand to optimize stock levels.
- Customer Segmentation: Grouping customers for targeted marketing campaigns.
4. Transportation:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely heavily on ML to perceive surroundings and make driving decisions.
- Route Optimization: Improving delivery and navigation routes.
- Predictive Maintenance: Anticipating failures in vehicles and infrastructure.
5. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Language Translation: Real-time translation services like Google Translate.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Providing conversational AI for customer service.
- Sentiment Analysis: Understanding public opinion on social media or reviews.
6. Manufacturing:
- Quality Control: Detecting defects through image analysis.
- Process Optimization: Improving production efficiency via predictive analytics.
- Predictive Maintenance: Monitoring machinery to predict breakdowns before they happen.
7. Cybersecurity:
- Threat Detection: Identifying malware or intrusion attempts.
- Anomaly Detection: Spotting unusual patterns that indicate potential security breaches.
- Automated Response: Enabling systems to respond quickly to threats.
How Machine Learning Works Along with Architecture
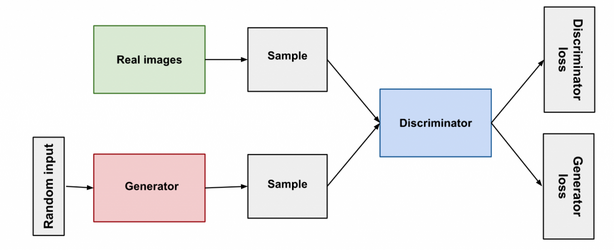
Machine learning systems operate through a pipeline of steps that transform raw data into actionable insights. The architecture of a machine learning system typically includes several layers and components, each playing a vital role:
1. Data Collection Layer:
Raw data is gathered from various sources such as sensors, databases, user interactions, or external APIs. This data may be structured (tabular data), unstructured (images, text), or semi-structured (logs, JSON).
2. Data Preprocessing Layer:
Data cleaning, normalization, and transformation happen here. Missing values are handled, outliers are removed or treated, and data is formatted into a consistent structure. Feature scaling (like normalization or standardization) ensures model convergence.
3. Feature Engineering Layer:
Critical for model performance, this step involves selecting, creating, or transforming input variables (features) that have predictive power. Feature selection techniques remove redundant or irrelevant variables to reduce complexity.
4. Model Selection Layer:
Based on the problem type (classification, regression, clustering), an appropriate machine learning algorithm is chosen. Common algorithms include:
- Linear and logistic regression
- Decision trees and random forests
- Support vector machines (SVM)
- Neural networks and deep learning models
5. Training Layer:
During training, the model iteratively adjusts its parameters to minimize a loss function, which quantifies the difference between predicted and actual outcomes. Techniques such as gradient descent help optimize the model.
6. Evaluation Layer:
The model is tested on validation or test datasets using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, or mean squared error to gauge its performance and generalizability.
7. Deployment Layer:
Once validated, the model is integrated into production systems where it can make real-time or batch predictions.
8. Monitoring and Maintenance Layer:
Ongoing monitoring detects model drift, where changes in data or environment degrade performance. Models are retrained or updated to maintain accuracy.
Typical Architecture Diagram:
[Data Sources] → [Data Preprocessing] → [Feature Engineering] → [Model Training] → [Evaluation]
↓ ↓
[Monitoring & Feedback] ←—————— [Deployment & Prediction]
Code language: CSS (css)Basic Workflow of Machine Learning
The journey from data to deployed ML model follows a well-defined workflow:
- Problem Definition:
Clearly define the objective (e.g., classify emails as spam or not spam). - Data Collection:
Gather relevant and sufficient data reflecting the problem domain. - Data Cleaning and Preprocessing:
Handle missing data, remove duplicates, normalize or standardize features. - Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA):
Analyze data distributions, detect correlations, and visualize features to understand patterns. - Feature Engineering:
Transform raw data into features that improve model learning—create new variables or reduce dimensionality. - Model Selection and Training:
Choose algorithms suitable for the task; train models on prepared data. - Model Evaluation:
Assess performance using cross-validation and metrics; tune hyperparameters. - Model Optimization:
Perform hyperparameter tuning with methods like grid search or random search. - Deployment:
Integrate the final model into software applications or services. - Monitoring and Maintenance:
Track model outputs, update models when performance drops, retrain with new data.
Step-by-Step Getting Started Guide for Machine Learning
Step 1: Build a Strong Foundation
Learn the fundamental mathematics underlying ML, including statistics, probability, linear algebra, and calculus. Gain proficiency in Python, the dominant language in ML.
Step 2: Understand Key ML Concepts
Study supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning paradigms. Familiarize yourself with concepts like overfitting, underfitting, bias-variance tradeoff, and regularization.
Step 3: Explore Popular ML Libraries
Get hands-on with libraries such as:
- Scikit-learn: Great for classical ML algorithms.
- TensorFlow and Keras: Popular for deep learning.
- PyTorch: Favored for research and flexibility in neural networks.
Step 4: Practice with Real Datasets
Begin experimenting with datasets from platforms like Kaggle, UCI ML Repository, or public government databases.
Step 5: Perform Data Preprocessing and EDA
Learn techniques for cleaning data, handling missing values, and visualizing data distributions.
Step 6: Implement Basic Algorithms
Start with simple models such as linear regression, logistic regression, and decision trees. Understand their assumptions and limitations.
Step 7: Evaluate and Tune Models
Use train-test splits, cross-validation, and performance metrics. Practice hyperparameter tuning to improve model accuracy.
Step 8: Progress to Advanced Topics
Explore neural networks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image data, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for sequential data, and reinforcement learning.
Step 9: Work on Projects and Competitions
Apply your skills to solve real-world problems, build portfolios, and learn from community feedback.
Step 10: Stay Current
Machine learning is a rapidly evolving field. Follow research papers, online courses, and community forums to keep your knowledge up to date.