MOTOSHARE 🚗🏍️
Turning Idle Vehicles into Shared Rides & Earnings
From Idle to Income. From Parked to Purpose.
Earn by Sharing, Ride by Renting.
Where Owners Earn, Riders Move.
Owners Earn. Riders Move. Motoshare Connects.
With Motoshare, every parked vehicle finds a purpose.
Owners earn. Renters ride.
🚀 Everyone wins.

What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source framework used primarily for automating web applications for testing purposes. It provides a suite of tools and libraries that allow users to interact with web browsers and simulate user actions like clicks, typing, navigation, and more. Initially developed by Jason Huggins in 2004, Selenium has since grown to become one of the most popular tools for web application testing. Selenium supports multiple programming languages such as Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and JavaScript, making it versatile for use with a variety of projects and programming environments.
Selenium can automate interactions with web applications across different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari, and more), and across different platforms (Windows, macOS, and Linux). Its ability to mimic user behavior in real browsers makes it an invaluable tool for quality assurance (QA) engineers, ensuring that web applications work as expected in various environments.
What are the Major Use Cases of Selenium?
- Functional Testing: The primary use case of Selenium is functional testing. This involves automating the validation of a web application’s functionality to ensure that it behaves as expected. Test cases can include verifying UI elements, form submissions, and navigation through the website.
- Regression Testing: Selenium helps in automating regression tests, which are used to verify that new changes in the web application haven’t caused any unintended side effects. Automation tools like Selenium can rerun the same test scripts repeatedly across different versions of an application.
- Cross-Browser Testing: With Selenium, users can run their tests across multiple browsers to ensure that their web application functions consistently on different platforms. This is crucial as web applications must work seamlessly on multiple browsers (like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.).
- Integration Testing: Selenium can also be used for integration testing, where different parts of the web application are tested together. This ensures that components interact with each other as expected when deployed together.
- Performance Testing: Selenium can assist in performance testing, although it is not its primary purpose. Automated scripts can help identify slow interactions and performance bottlenecks when simulating user behavior.
- Data-Driven Testing: With Selenium, you can use data-driven testing techniques where the same test case is executed multiple times with different data inputs. This is ideal for testing forms or submission workflows.
How Selenium Works Along with Architecture?
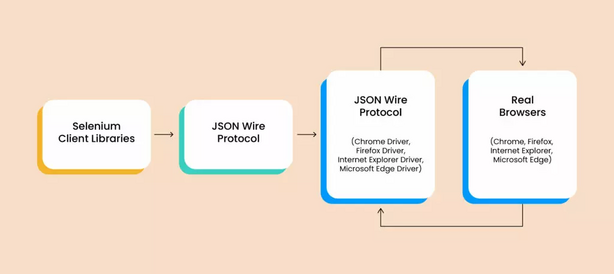
Selenium operates based on a client-server architecture, and its working mechanism involves multiple components interacting with each other. Here’s a breakdown:
- Selenium WebDriver: The WebDriver is the core component of Selenium. It provides a programming interface to control the browser. It interacts directly with the web browser (via native OS APIs) to simulate real user actions, like clicking, typing, or navigating.
- Selenium Server: For browsers that require remote interaction, Selenium Server acts as an intermediary between the Selenium WebDriver and the browser. It is also used when running tests on a grid or distributing tests across multiple machines.
- Selenium Grid: Selenium Grid enables parallel test execution across multiple machines and browsers. It allows tests to run on different combinations of browsers, operating systems, and environments simultaneously, speeding up the testing process.
- Selenium IDE: Selenium Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a record-and-playback tool for Selenium. It allows users to create test scripts by interacting with the browser through a simple graphical interface, making it useful for beginners or those who are not familiar with programming.
- Browser Drivers: Selenium communicates with various browsers using browser-specific drivers. For example, Chrome uses the ChromeDriver, and Firefox uses GeckoDriver. These drivers are responsible for translating Selenium commands into actions that the browser can understand and execute.
What are the Basic Workflow of Selenium?
The basic workflow of Selenium involves several steps:
- Setup the Test Environment: First, you need to install Selenium WebDriver and the necessary browser driver (e.g., ChromeDriver for Google Chrome) and programming language bindings (Java, Python, etc.).
- Write Test Scripts: After setting up the environment, you write test scripts using your preferred programming language. These scripts instruct Selenium WebDriver to open a browser, interact with web elements, and validate results.
- Executing Tests: Once the scripts are ready, you execute them either locally or using a Selenium Grid for parallel execution. Selenium WebDriver communicates with the browser and performs actions like clicking buttons, filling out forms, or verifying page content.
- Test Results and Reporting: After running the tests, you collect results, check for errors or failures, and generate reports. These reports can be used to analyze the performance and behavior of the application.
- Continuous Integration: Selenium can be integrated into Continuous Integration (CI) systems, allowing automated testing to run every time new code is pushed to the repository, ensuring that the application is continuously validated and no new issues are introduced.
Step-by-Step Getting Started Guide for Selenium
1. Install Java Development Kit (JDK): Selenium WebDriver supports multiple programming languages, but Java is one of the most commonly used. Therefore, you first need to install the Java Development Kit (JDK) if you plan to use Java. You can download it from the official Oracle website.
2. Set up an Integrated Development Environment (IDE): Choose an IDE like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA for Java development. Install the necessary plugins and configure the Java environment.
3. Download and Set up Selenium WebDriver: Download the Selenium WebDriver for your chosen language from the official Selenium website. Then, add the WebDriver JAR files to your project as dependencies.
4. Download Browser Driver: Selenium WebDriver interacts with browsers through browser-specific drivers. For example, to automate Chrome, download ChromeDriver and ensure it’s in your system’s PATH or specify the location in your script.
5. Write Your First Test Script: Create a simple test script in your chosen language (Java, Python, etc.). Here’s an example using Java:
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class FirstSeleniumTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set path to ChromeDriver
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "path/to/chromedriver");
// Create an instance of the Chrome WebDriver
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
// Navigate to a webpage
driver.get("https://www.google.com");
// Perform actions like searching
System.out.println("Title: " + driver.getTitle());
// Close the browser
driver.quit();
}
}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)6. Run the Test: Run the script, and it will launch the browser, navigate to the URL, print the page title, and close the browser.
7. Automate More Complex Tasks: Once you’re comfortable with the basic automation, you can move on to more complex tasks like handling forms, drop-downs, or interacting with dynamic content.
8. Explore Additional Selenium Features: Selenium has advanced features such as handling browser pop-ups, mouse movements, screenshots, and managing waits to handle dynamic elements.
By following these steps, you can get started with Selenium and automate your testing process, ensuring faster and more reliable test execution.