MOTOSHARE 🚗🏍️
Turning Idle Vehicles into Shared Rides & Earnings
From Idle to Income. From Parked to Purpose.
Earn by Sharing, Ride by Renting.
Where Owners Earn, Riders Move.
Owners Earn. Riders Move. Motoshare Connects.
With Motoshare, every parked vehicle finds a purpose.
Owners earn. Renters ride.
🚀 Everyone wins.
What are the 10 features of kubernetes ?
- container orchestrator
- Workload placement
- Maintains desired state
- Self-healing
- Automated rollbacks
- Auto scaling
- Load balancing
- Speed of deployment
- Ability to absorb change quickly
- Hide complexity in the cluster
How Kubernetes works ?
Kubernetes are comprised of master and multiple nodes where Master is In-charge of cluster which manages nodes and nodes manages one or multiple pods and pod manages one or multiple containers.
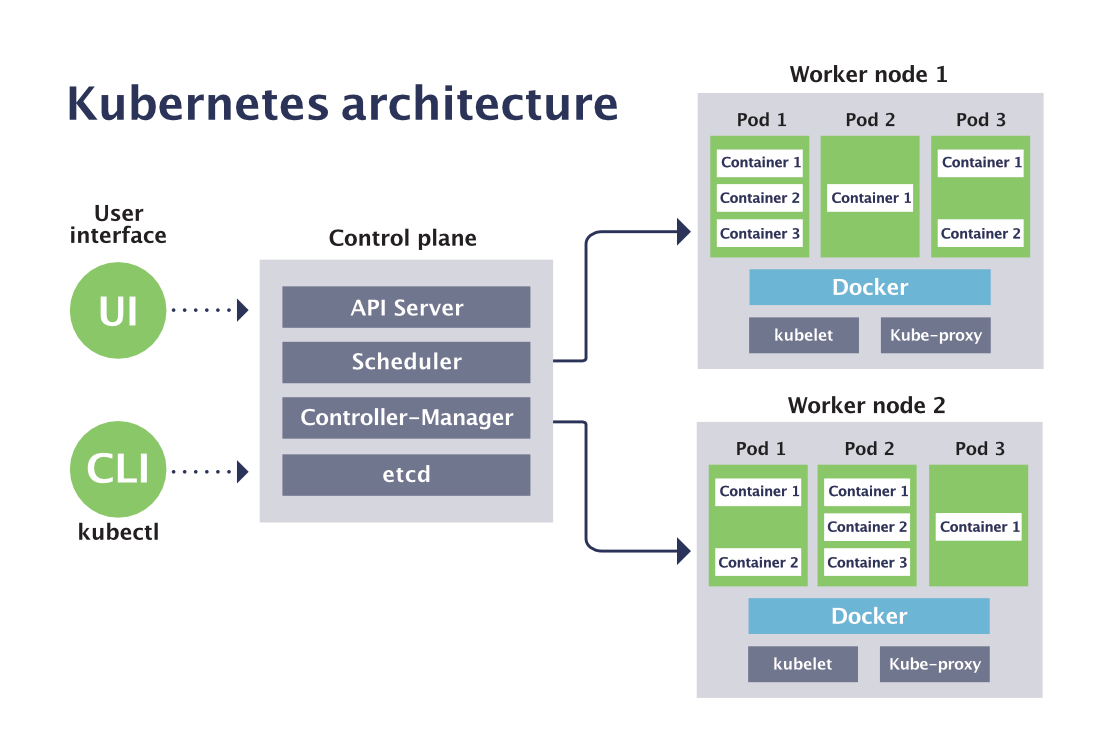
What are the components of Master ?
- Kube-API server – front end thru which any communication is passed and consumes JSON via manifest files.
- Kube-Cluster store – requests gets stored in cluster store in key value format powered by etcd.
- Kube-Controller manager – controller of controllers which watches for changes and helps in maintaining desired state.
- Kube-Scheduler – watches API server for new pods, assigns work to nodes and interacts with kubelet in node.
What are the components of Worker ?
- Kubelet – main kubernetes agent which registers node with cluster and instantiates pods, exposes endpoint on: 10255.
- Container Engine (Docker) – does container management: pulling images and running containers.
- Kube –proxy – manages kubernetes networking (pod IP addresses), all containers in a pod share a single IP.
What are the components of Workstation ?
Kubectl – CLI to interact with APIserver
What is POD ?
A pod is the smallest execution unit that you can create and manage in Kubernetes. A Pod is a group of one or more containers, with shared storage and network resources, and a specification for how to run the containers.
- A pod encapsulates one or more applications.
- When a pod is created it is assigned its own unique IP address.
- Pods have a single IP address that is applied to every container within the pod.
- Containers in a pod share the same resources such as memory and storage (All containers in pod share the pod environment).
- If there are multiple containers within the pod, they can communicate between each other simply by using localhost. Communications outside of the pod is achieved by exposing a port.
- If a pod (or the node it executes on) fails, Kubernetes can automatically create a new replica of that pod to continue operations.
- Communications between pods in a cluster takes advantage of the fact that Kubernetes assigns a cluster-private IP address to every pod in a cluster, eliminating the need to either explicitly create links between pods or to map container ports to host ports.
- Pods utilize an agent on each node called a kubelet to communicate with the Kubernetes API and the rest of the cluster.
- As the load on a pod increases, Kubernetes can automatically replicate the pod to achieve desired scalability.
- multi-container pods ease deployment configuration compared to setting up shared resources between containers on your own.